Baphomet: Baphomet is a symbolic, hybrid figure from Western occult traditions, depicted with both human and goat features.
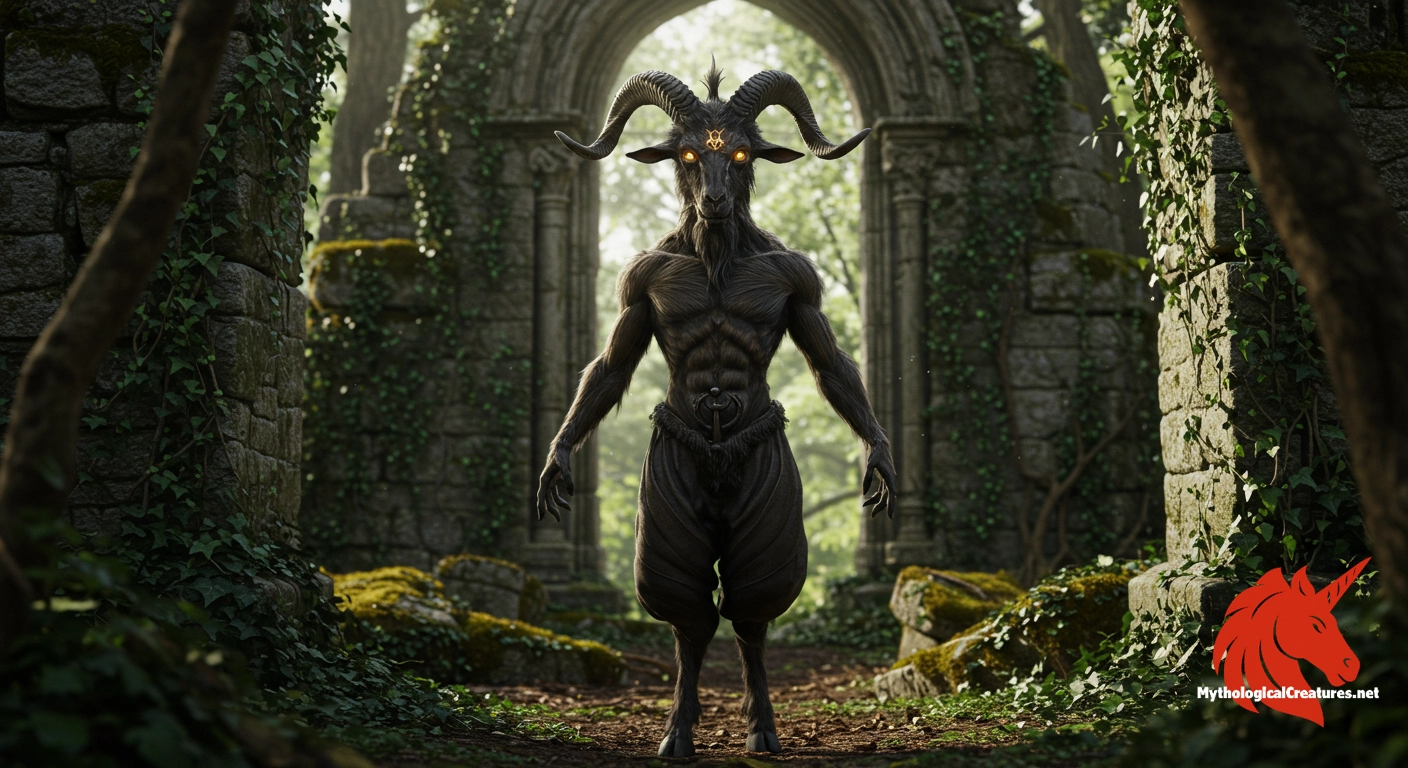
Baphomet
Baphomet - Baphomet embodies the equilibrium of opposites and represents the aim of perfect social order within occult philosophy.
Origins & First Encounters
Baphomet is a complex figure that bridges medieval superstition with modern esoteric interpretation. Its roots can be traced to the turbulent era of the early 14th century, when accusations against the Knights Templar brought the name into infamy. The emerging iconography was steeped in the charged atmosphere of heresy trials and shifting religious allegiances. Over time, the figure evolved into a symbol that embodies the reconciliation of opposites, merging attributes of light and darkness. The image of Baphomet has been reinterpreted by various groups, reflecting diverse cultural and mystical paradigms. This synthesis of conflicting elements provided a unique lens through which balance and duality could be understood. As such, its cultural resonance spans from medieval spirituality to contemporary countercultural movements. The allure of Baphomet lies in its ambiguous identity and the enduring mystery that surrounds its origins. Today, it continues to captivate and challenge those who seek to explore the deeper symbolism hidden within myth and art.
Source Texts & Tale Variants
Medieval records of the Knights Templar trials provide one of the earliest textual mentions of Baphomet, though these accounts were invariably influenced by the intense religious conflicts of the period. Numerous trial records reveal that the Order was accused of venerating an enigmatic figure, which later became synonymous with the name Baphomet. The sparse details in these documents have given rise to a wealth of speculation and reinterpretation over the centuries. In the 19th century, figures such as Éliphas Lévi revitalised interest through detailed illustrations and philosophical writings that redefined the figure as a symbol of equilibrium. Occult treatises and grimoires further enriched the narrative with interpretations that ranged from diabolic imagery to metaphysical ideals. The multiplicity of these sources has ensured that the story of Baphomet remains multifaceted and open-ended. Variations in narrative detail highlight the role of bias and interpretation in historical documentation. Modern occult literature and scholarly debates continue to draw from these early accounts, weaving them into a broader tapestry of myth and mystery. Consequently, Baphomet’s legend is sustained by a diversity of primary sources and divergent story variants that evolve with each retelling.
Form & Powers
Baphomet is most commonly depicted as a striking blend of human and animal characteristics, with a goat’s head and a humanoid body blending seamlessly into one form. The face is marked by prominent, crescent-shaped horns and a finely detailed beard that underscores an aura of ancient wisdom and enigma. Its eyes and facial expression often exude a calm yet penetrating intensity, inviting observers to question the boundaries between the mortal and the mystical. Intricate details, such as the inclusion of a small flame or torch on its head, symbolise insight and the illumination of hidden truths. The body of Baphomet is rendered with both muscular and soft contours, suggesting the merger of masculine vigour and feminine grace. Elaborate robes or drapery, frequently adorned with cryptic symbols, further accentuate the dual nature of the entity. The figure is typically shown with expansive wings or stylised representations of flight, representing the transcendence of ordinary physical limits. Artists have played with variations in scale and posture, each rendition offering subtle nuances that reflect different facets of its dual identity. This carefully constructed visual language continues to inspire reinterpretations in both traditional art forms and modern digital media.
Regional Faces
Baphomet’s image has travelled far beyond its European medieval origins, taking on diverse interpretations in different geographical regions. In France, where much of modern occultism was reinvigorated during the 19th century, the figure is often seen as a profound emblem of philosophical balance and mystery. British esoteric societies have embraced the figure as an intriguing amalgam of contradictions, weaving its image into the fabric of ritualistic practice and symbolic inversion. In North America, contemporary occult and countercultural movements have reimagined Baphomet as a symbol of liberation from traditional constraints and oppressive dogma. Urban artists and cultural commentators in various cities have adopted its imagery to critique societal norms and celebrate nonconformity. Even within parts of the modern Middle East, where mystical allegory interacts with ancient traditions, adaptations of Baphomet echo the local narrative of duality and balance. Regional art exhibits and literary works further embellish its form to reflect local mythos and spiritual ideologies. The diversity of these regional adaptations underscores the flexibility with which Baphomet’s symbolism can be molded. Such variations ensure that the figure remains a living symbol, continually reshaped by the cultural and social reflections of its interpreters.
Cultural Parallels
An examination of global mythological figures reveals that Baphomet shares thematic elements with several horned deities and dualistic archetypes. Comparable to the enigmatic Celtic Horned God, Baphomet emerges as a representation of nature’s raw, untamed energy and the cycle of life and death. Similar to the ambiguous qualities found in depictions of Pan or satyrs, the figure simultaneously evokes fertility, liberation, and the wild forces of the natural world. The synthesis of masculine and feminine traits in Baphomet is reminiscent of broader mythological motifs that celebrate the union of opposites. This duality is not unique, as many spiritual systems, such as those encapsulated in Taoist yin and yang, strive to illustrate the balance of divergent forces. While Baphomet does not have a direct counterpart in every tradition, its synthesis of diverse qualities resonates with universal themes of contradiction and harmony. In some interpretations, the figure’s ambiguous nature is seen as a mirror reflecting both the light and dark aspects of humanity. Cross-cultural dialogues about deities and symbolic figures regularly invoke Baphomet as an emblem of the mysterious and the ineffable. Such comparative analysis reinforces the idea that symbols of duality tightly interlace mythologies across the world, inviting ongoing exploration of their meaning.
Legacy & Modern Evolution
Baphomet’s historical evolution mirrors the shifting landscapes of power, belief, and artistic expression over the centuries. Initially entangled in the accusations levied against the Knights Templar, the figure was once seen primarily as a mark of diabolic influence and heresy. By the mid-19th century, the reimagining of the form by occult scholars, especially through the work of Éliphas Lévi, transformed it into a nuanced symbol representing the synthesis of opposites. In this reinterpretation, Baphomet came to embody a quest for spiritual equilibrium and the harmonious balance between divergent forces. The symbolic legacy of this figure has continued to grow, influencing the iconography of modern occult movements and alternative spiritualities. Contemporary art and literature frequently resurrect Baphomet as a provocative emblem of rebellion against established societal norms. Its imagery resonates with those who challenge traditional dichotomies, inviting dialogue about the nature of good, evil, and the spaces in between. In modern popular culture, representations of Baphomet span a spectrum from subversive artistic expression to commercial motifs within music and fashion. This dynamic evolution reiterates the timeless human fascination with symbols that capture the complex interplay of darkness and light, order and chaos.
Interesting Fact
An intriguing aspect of Baphomet is how its striking dual nature—simultaneously demonic and deeply symbolic—has allowed it to be embraced by a wide spectrum of occult and mystical traditions, each interpreting its meaning in diverse ways.
Quick Creature Info
Associations:
Our Mythic Legendary Rating:

Also Sometimes Known As:
Supernatural Powers:
Physical Attributes:
Abilities:
Behavior:
Lore:
Related Creatures, Tales or Lore
References
Discover Another Mythical Legend You May Not Have Heard Of?
Uncover the mysteries of ancient folklore and expand your knowledge of legendary beings from cultures around the world.
Dare to Meet the Empusa....
Mythical Disclaimer: The images and data on this site are derived from various historical and literary sources, but we have found that many myths often have multiple versions and interpretations across references, sometimes contradictory. As a result, these creature depictions are artistic interpretations—imaginative blends of folklore, legend, and a dash of AI guesswork. Because creature descriptions vary widely, our illustrations and accompanying information represent our best effort to honor mythology while bridging creative gaps. Enjoy these interpretations—just remember, we've done our best to respect the stories and validate available data, but in the realm of mythology, details often shift, imagination leads the way, and nothing is ever set in stone!
Curated by the Mythological Creatures Team (rev. May 2025)
